Civil Engineering Program
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
OVERVIEW
Bachelor of Engineering (Civil Engineering)
B.Eng. (Civil Engineering)
Program Overview
The Civil engineering department of Srinakharinwirot University has grown substantially since its formation in 1993. Recently, with increasing environmental problems and concerns, the department was changed to Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. There are two programs in our CVE Department, namely Civil Engineering program (CE) and Environmental Engineering program (EvE). At present, only the Civil Engineering program is seeking accreditation from ABET. Per the requirments set by the Ministry (MHESI), all academic programs need to be revised or updated every 5 academic years to keep up with the latest technology and the needs of the industry.
For more Information: https://cve.eng.swu.ac.th/en/abet-2024-en/
VISION
The vision is to bring the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering towards academic and professional excellence and to contribute to the community for sustainable development.
MISSION
The mission of the Civil and Environmental Engineering at the Srinakharinwirot University, CVE-SWU, aims to create proactive civil engineers who have the knowledge both in theory and practice, morals, and ethics needed in the engineering profession. CVE-SWU is committed and dedicated to the missions of teaching, research, and academic service. We are also engaged in knowledge acquisition, applications, state-of-the-art techniques, and technologies as well as motivating the students with the values of lifelong learning.
PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES (PEOs)
- Graduates successfully engage in the practice of Civil Engineering within industry, government, and private practice, working toward sustainable solutions in a wide array of technical specialties including construction, environment, geotechnical, surveying, structures, transportation, and water resources.
- Graduates employ their leadership skills toward professional growth and development such as pursuing advance study in engineering, professional registration, and continuing education. Some graduates transition into other professions, such as entrepreneur, education, business, and law through further education.
- Graduates provide service to society and engineering profession through membership and participation in professional societies, government, educational institutions and civic organizations.
The above Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) of our Civil Engineering program are published on our Civil and Environmental Engineering Website: https://cve.eng.swu.ac.th/en/abet-2024-en/
Student Outcomes (SOs)
- an ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science, and mathematics
- an ability to apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental, and economic factors
- an ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences
- an ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts
- an ability to function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives
- an ability to develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data, and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions
- an ability to acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
RESEARCH
The department’s research current active research topics include: bridge structure, geotechnical engineering, concrete technology, materials testing ,infrastructure engineer, construction engineering management and wastewater treatment, with funding support from various sources including the National Science Foundation (NSF), as well as state and federal agencies.
PROGRAM OF STUDY
The Civil Engineering curriculum has been deliberately designed in the flowchart of our program curriculum is illustrated in Figure 1. The prerequisite structure of the program’s required courses are also presented in Figure 1. as arrow lines. These prerequisite requirements are also regulated by the Council of Engineering of Thailand (https://en.coe.or.th/).
Structure of the Curriculum
B.Eng. (Civil Engineering)
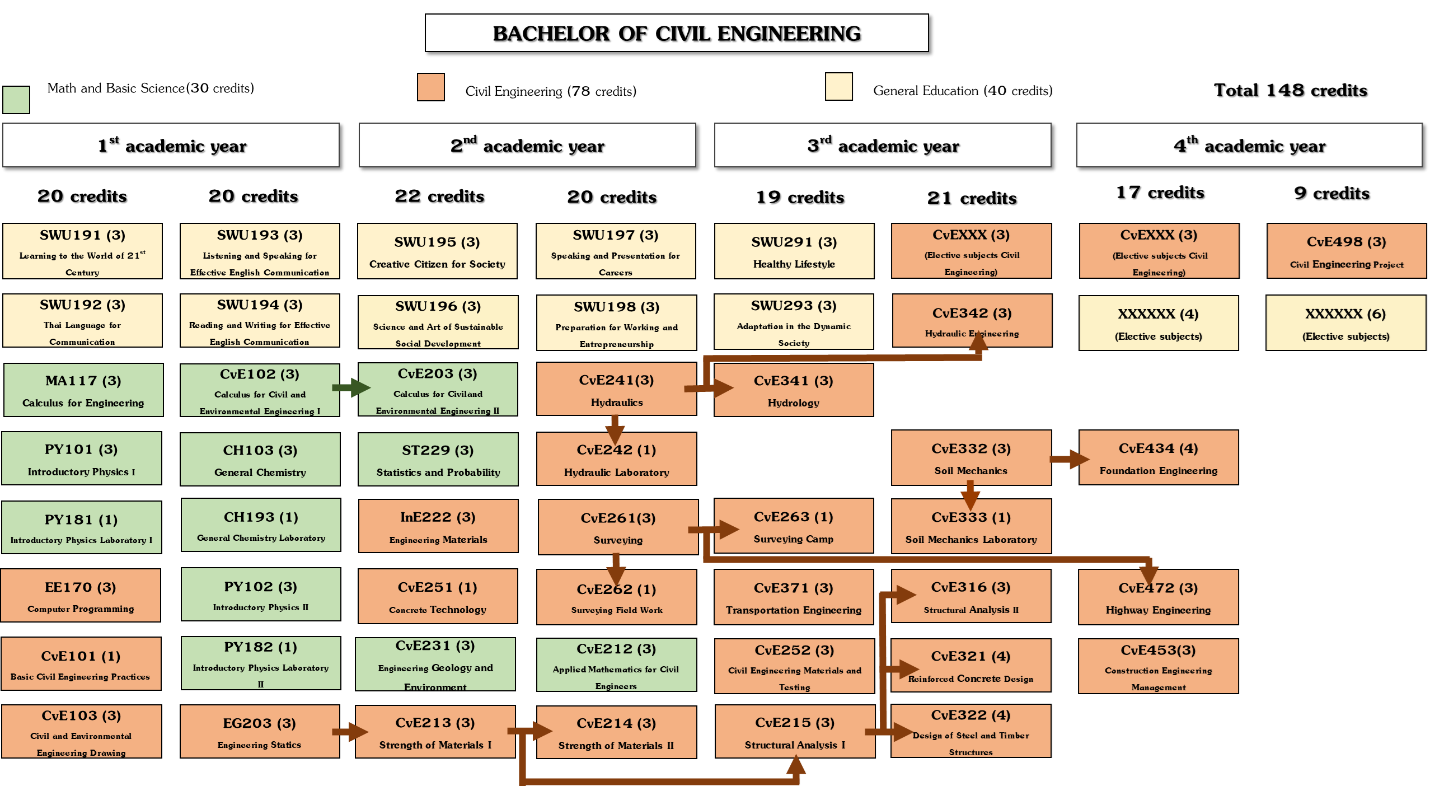
Figure 1. the flowchart of Civil Engineering program curriculum
Bachelor of Civil Engineering Curriculum
|
Course (Department, Number, Title)
List all courses in the program by term starting with the first term of the first year and ending with the last term of the final year. |
Required, R
Elective, E or a Selected Elective, SE.1 |
Subject Area (Credit Hours) | |||||
| Math & Basic Sciences |
Engineering Topics; Check if Contains Significant Design (√) |
Other | |||||
| 1st semester of First academic year | |||||||
| SWU191 Learning to the World of 21st Century | R | 3 | |||||
| SWU192 Thai Language for Communication | R | 3 | |||||
| MA117 Calculus for Engineering | R | 3 | |||||
| PY101 Introductory Physics I | R | 3 | |||||
| PY181 Introductory Physics Laboratory I | R | 1 | |||||
| EE170 Computer Programming | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE101 Basic Civil Engineering Practices | R | 1 | |||||
| CVE103 Civil and Environmental Engineering Drawing | R | 3 | |||||
| 2nd semester of First academic year | |||||||
| SWU193 Listening and Speaking for Effective English Communication | R | 3 | |||||
| SWU194 Reading and Writing for Effective English Communication | R | 3 | |||||
| CH103 General Chemistry | R | 3 | |||||
| CH193 General Chemistry Laboratory | R | 1 | |||||
| PY102 Introductory Physics II | R | 3 | |||||
| PY182 Introductory Physics Laboratory II | R | 1 | |||||
| CVE 102 Calculus for Civil and Environmental Engineering I | R | 3 | |||||
| EG203 Engineering Statics | R | 3 | |||||
| 1st semester of Second academic year | |||||||
| SWU195 Creative Citizen for Society | R | 3 | |||||
| SWU196 Science and Art of Sustainable Social Development | R | 3 | |||||
| ST229 Statistics and Probability | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE203 Calculus for Civil and Environmental Engineering II | R | 3 | |||||
| INE222 Engineering Materials | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE213 Strength of Materials I | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE251 Civil Engineering Materials and Testing | R | 1 | |||||
| CVE231 Engineering Geology and Environment | R | 3 | |||||
| 2nd semester of Second academic year | |||||||
| SWU197 Speaking and Presentation for Careers | R | 3 | |||||
| SWU198 Preparation for Working and Entrepreneurship | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE212 Applied Mathematics for Civil Engineers | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE214 Strength of Materials II | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE241 Hydraulics | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE242 Hydraulic Laboratory | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE261 Surveying | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE262 Surveying Field Work | R | 1 | |||||
| 1st semester of Third academic year | |||||||
| SWU291 Healthy Lifestyle | R | 3 | |||||
| SWU292 Adaptation in the Dynamic Society | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE215 Structural Analysis I | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE252 Concrete Technology | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE263 Surveying Camp | R | 1 | |||||
| CVE341 Hydrology | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE371 Transportation Engineering | R | 3 | |||||
| 2nd semester of Third academic year | |||||||
| CVE316 Structural Analysis II | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE321 Reinforced Concrete Design | R | 4 | |||||
| CVE322 Design of Steel and Timber Structures | R | 4 | |||||
| CVE332 Soil Mechanics | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE333 Soil Mechanics Laboratory | R | 1 | |||||
| CVE342 Hydraulic Engineering | R | 3 | |||||
| CVExxx (Major selective) | SE | 3 | |||||
| 1st semester of Final academic year | |||||||
| CVE434 Foundation Engineering | R | 4 | |||||
| CVE453 Construction Engineering Management | R | 3 | |||||
| CVE472 Highway Engineering | R | 3 | |||||
| CVExxx (Major selective) | SE | 3 | |||||
| Xxxxxx (Free selective) | E | 4 | |||||
| 2nd semester of Final academic year | |||||||
| CVE498 Senior Project (Capstone Project) | R | 3 | |||||
| Xxxxxx (Free selective) | E | 6 | |||||
| TOTALS (in terms of semester credit hours) | 30 | 78 | 40 | ||||
| OVERALL TOTAL CREDIT HOURS FOR COMPLETION OF THE PROGRAM | 148 | ||||||
| Percent of Total | 20.40% | 53% | 26.60% | ||||
|
Total must satisfy
minimum credit hours |
Minimum Semester Credit Hours | 30 Hours | 45 Hours | ||||
Program Structure Flowchart
The flowchart of our program curriculum is illustrated in Figure . The prerequisite structure of the program’s required courses are also presented in Figure as arrow lines. These prerequisite requirements are also regulated by the Council of Engineering of Thailand (https://en.coe.or.th/)

PERIODIC REVIEW OF PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES :
The program is scheduled to be reviewed periodically with the following frequency and means for each constituency as shown in Table .
Table Schedule of periodic review of Program Educational Objectives
| Constituency | Frequency | Means |
| Faculty | As needed | Department Meeting |
| Student | Annually | Exit Survey |
| Alumni | Every 3 years | Survey |
| IAB | Every 3 years | Meeting / Survey |
| Employers | Every 3 years | Focus group / Survey |
Students’ exit survey of graduating students is used as an indirect assessment tool for the 7 student outcomes. The students’ exit survey is usually conducted prior to student graduation. The survey questions primarily focus at the attainment of the 7 student outcomes that students should gain from our program. The results of the exit survey in academic years 2023 are provided in Tables bolow
Summary of the Students’ Exit survey for academic year 2021 – 2023.
| Year | SO1 | SO2 | SO3 | SO4 | SO5 | SO6 | SO7 |
| 2023 | 10/10 = 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 2023 | 16/17 = 94.1% | 100% | 94.10% | 94.10% | 94.10% | 94.10% | 94.10% |
| 2023 | 37/40 = 92.5% | 90% | 85% | 97.50% | 97.50% | 95% | 95% |
The employors’ survey is generally conducted annually. The surveying questions for the employors typically inquire about the ability of our graduates to works successfully for the industry. The results of the employor survey for academic years 2023 are provided in Table below.
Summary of the Employor survey for academic year 2023.
| Year | SO1 | SO2 | SO3 | SO4 | SO5 | SO6 | SO7 |
| 2023 | 85.7% | 85.7% | 85.7% | 100% | 100% | 85.7% | 100% |
Number of Enrolled Students and Graduates (CE)
| Academic Year | Enrolled Students | Graduates |
| 2016 | 50 | 41 |
| 2017 | 48 | 40 |
| 2018 | 46 | 39 |
| 2019 | 46 | 39 |
| 2020 | 45 | 45 |
| 2021 | 43 | 4th year |
| 2022 | 35 | 3rd year |
| 2023 | 50 | 2nd year |
PROGRAM CHAIR
Attasit Sirivachiraporn, D.Eng.
(Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand)
Lecturer
Soil mechanics, Foundation engineering, Engineering geology
Faculty
Ittiporn Sirisawat, PhD
(Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, Thailand)
Associate Professor
Civil Engineering Materials and Testing, Construction Engineering Management, Highway Engineering
Chanwit Saiyudthong, PhD
(The University of Sheffield, UK)
Associate Professor
Advanced Domestic Wastewater Process, Diameter and surcharge effects on solute transport across surcharged manholes
Sudniran Phetcharat, D.Eng.
(Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand)
Associate Professor
Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems, GIS, Flexible Pavement on the Affected of Traffic
Suniti Suparp, D.Eng.
(Kasetsart University, Thailand)
Associate Professor
The bridge live load models, structural engineer, infrastructure engineer
Treerapot Siripirote, PhD
Assistant Professor
(The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China)
Transportation engineering, Numerical analysis for engineer, Advanced mathematics for civil engineering
Panuwat Joyklad, PhD
(Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, Thailand)
Associate Professor
Structural engineer, Bridge design engineer, Infrastructure and Rail Transportation Structural System
Setta Sasananan, PhD
(University of Tasmania, Australia)
Lecturer
Water Supply and Sanitary Engineering, Timber and Steel Design
Attasit Sirivachiraporn, D.Eng.
(Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand)
Lecturer
Soil mechanics, Foundation engineering, Engineering geology
Pradthana Prachanurak, D.Eng.
(Kasetsart University, Thailand)
Lecturer
Engineering Geology, Solid waste Engineering, Biology for Environmental Engineering, Hazardous Waste Engineering
Piyanuch Jaikaew, PhD
(Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan)
Assistant Professor
Unit Operation for Environmental Engineering , Environmental System Management, Environmental Impact Assessments Cleaner technology, Life cycle analysis, water footprint, SGDs, and Hydraulic Engineering
Suthida Theepharaksapan, PhD
(University of Tokyo, Japan)
Assistant Professor
Statistical Methods for Environment and Water Resources, Environmental System and Management, Water reuses by membrane
Siriwan Srisorrachatr, PhD
(Mahidol University, Thailand)
Associate Professor
Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, Wastewater treatmen
Suppachai Sinthaworn, D.Eng.
(Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand)
Associate Professor
Structural Engineering, Earthquake Engineering, Concrete Technology and Construction Materials.
Contact
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Faculty of Engineering, Srinakharinwirot University,
C Bldg., 63, M.7, Rangsit-Naknon Nayok Rd., Ongkharak,
Nakhon Nayok, 26120, THAILAND
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Suppachai Sinthaworn
Tel : +662 649 5000 ext. 27065
E-mail address : suppachai@g.swu.ac.th
